Types of Network
Types of Networks: LAN, MAN, WAN and the Internet
Computers connected by many different technologies. An are interconnection between more than one computer,
over a virtual and shared connection, in a client-to-server or peer-to-peer manner is called a network. That
is to say, so that the flow of information is accommodated, computer resources are connected using networks.
This is just the opposite of the old terminal-to-host hardwired connection. Although a network can support
terminal-to-host connections through terminal emulators or a terminal server, it offers a lot more
flexibility in switching connections. The disadvantage of this explosion in terms of sharing information
arises when one computer wishes to share its information system with another which has different network
protocols and different network technology. As a result, even if you could agree on a type of network
technology to physically interconnect the two computers at different locations, your applications still
would not be able to communicate with each other because of the different protocols.
A very basic question arises about the requirement of networks. This may be justified with the help of the
following points:
- Sharing of resources can be easily done.
- Reliability: There is no central computer, so if one breaks down you can use others.
• Networks allow you to be mobile.
The term networking applies to:
- The exchange of information among institutions, groups or individuals.
- The process of data communications or electronic voice.
Local Area Network The Local Area Network (LAN) technology connects machines and people within a site. LAN is a network that is restricted to a relatively small area as shown in Figure 9. LANS can be defined as privately-owned networks offering reliable high speed communication channels that are optimized to connect information processing equipment in a small and restricted geographical area, namely, an office, a building, a complex of buildings, a school or a campus.
A LAN is a form of local (limited-distance), shared packet network for computer communications. LANs interconnect peripherals and computers over a common medium so that users are able to share access to peripherals, files. databases, applications and host computers. They can also provide a connection to other networks either through a computer, which is attached to both networks, or through a dedicated device called a gateway.
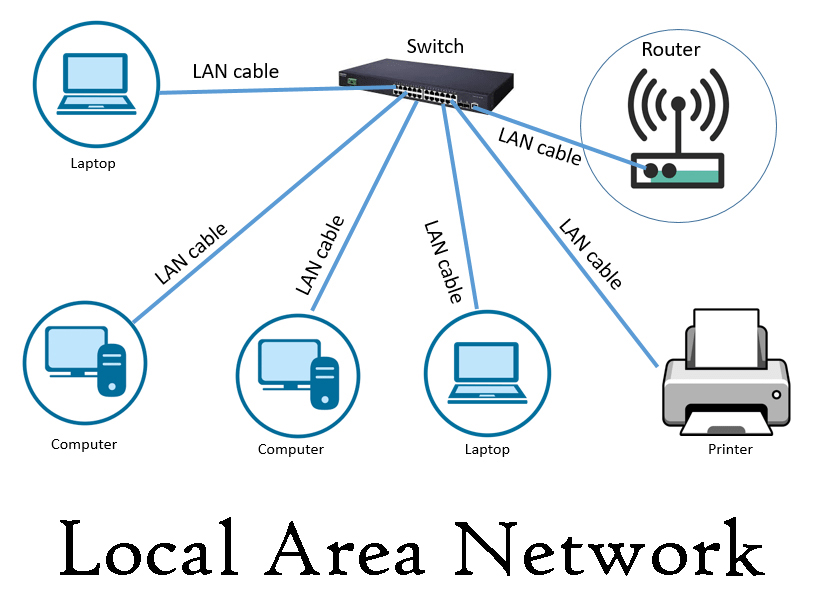
The components used by LANs can be categorized into hardware, cabling protocols and standards. Various LAN protocols are Ethernet, Token Ring: Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), NetBIOS and NetBeui, TCP/IP, Fiber Distributed data interchange(FDDI),SMB and IPX/SPX.
Metropolitan Area Network
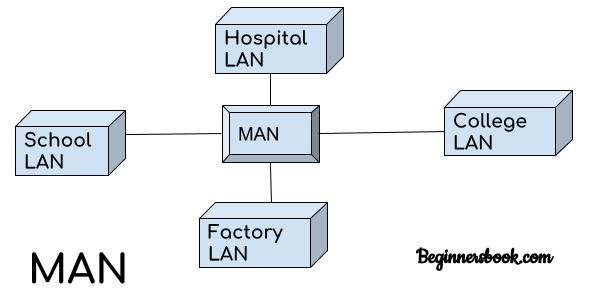
Such large geographic areas districts, towns cities by Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). linking or
interconnecting smaller networks within large geographic area, information conveniently distributed
throughout the network. Local libraries and government agencies use MAN to establish a link with private
industries and citizens. also connect MANS together within a larger area than: LAN. The geographical limit
of a MAN may span city. figure depicts how a MAN may be available within a city.
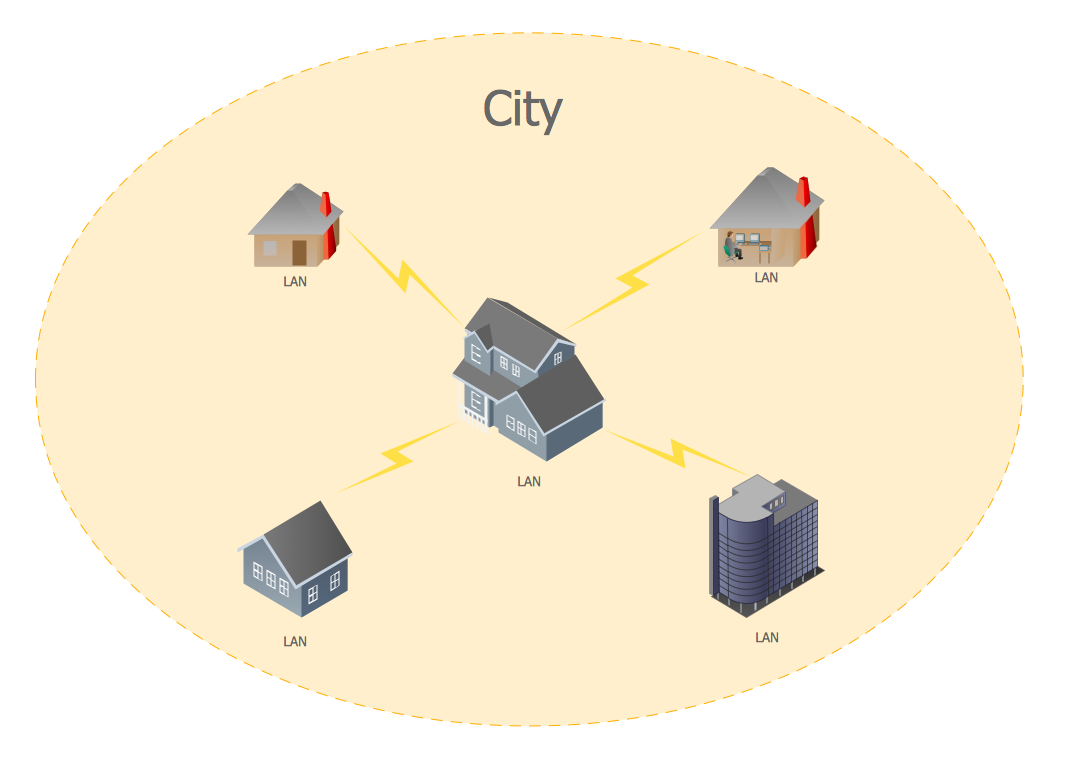
In MAN, different LANS connected through local telephone exchange. Some of the widely protocols MAN are ATM RS-232, OC-3 lines Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), Frame Relay, Integrated Services Network (ISDN) and Mbps), etc. These protocols are quite different from those used LANs.
Wide Area network
This technology connects sites that are in diverse locations. Wide Area Network (WANs) connects such as
large geographic areas, the world, India or New Delhi. There is no geographical limit of WAN. This kind of
network can be connected by using satellite uplinks or dedicated transoceanic. Hence, a a WAN be defined as
a data communications network covering a relatively broad geographical area to connect LANS together between
different cities with the help of transmission facilities provided by common carriers, such as telephone
companies. WAN technologies operate at the lower three layers of the OSI may
reference model. These are the physical data link and network layers.
Figure explains the WAN, which connects many LAN together. It also uses switching technology provided by
local exchange and long distance carrier.

Packet switching technologies, such as Frame Relay, SMDS, ATM and X.25 are used to implement WAN
along with statistical multiplexing to allow devices to use and share these circuits.
| LAN | WAN | |
|---|---|---|
| Example | The network in an office building can be a LAN | The Internet is a good example of WAN |
| Technology | Tend to use certain connecitivity technologies, primearly Ethernet and Token Ring. | Tends to use technologies like MPLS, ATM, Frame Relay amd X.25 for connectivity over longer distances. |
| Connection | One LAN can ve connected to other LANs over any distance via telephone lines and radio waves. | Computer connected a wide-area network are often connected through public networks, such as the telephone system. Thewy vcan also connected through leased lines or satelites. |
| Components | Layers 2 devices like swithche s and bridges. Layer I device l8ike hubs and repeateres. | Layers 3 device Routers, Multi-layers Sweitchs and Tehnology specific devices like ATM or Frame-relay Switches etc. |
| Fault Tolerance | LANs tend to have fewer problems associated with them, as there are smaller nuof systems to deal with. | WANS tend to be less fault tolerant as they consist of large number of systems. |
| Data Transmission Error | Experiences fewer data transmission Errors. | Experiences more data transmission error a s compares to LAN. |
| Ownership | Typocallly owned, com=nntrolled, and managed by a single person or organization. | WANs (like the Internet) are not owned by any one organisation but rather exist under collective ior distributed ownership an management over long distances. |
| Geographical Spread | Have a small geographical range and do not need any leased Telecommunication lines. | Have a large geographical range generally spreading across boundaries and need leased Telecommunication lines. |
| Maintenance Costs | Because it Covers a relatively small geographical area, LAN is easier to maintain at ralatively low costs | maintaining WAN is diffucilt because os its wides geogeraphical coverage and higher maintenance costs. |
| Bandwidth | High bandwidth is available for transmission. | Low bandwidth is available for transmission. |
| Congestion | Less Congestion | High Congestion |